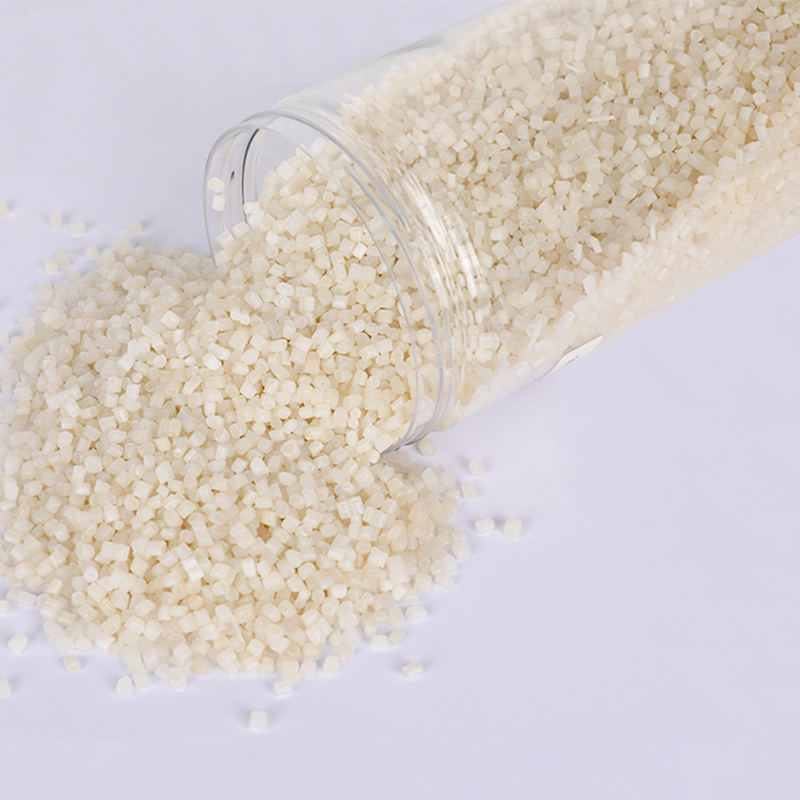
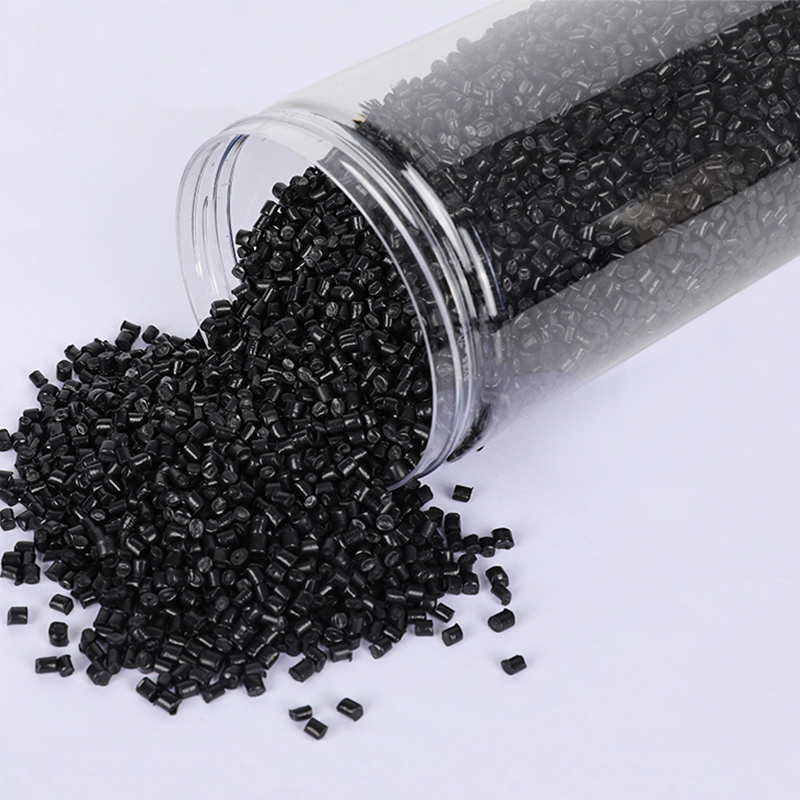
Stay up to date with our recent products
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Best Practices for Handling and Processing Recycled Polyethylene in Industrial Settings
Recycled polyethylene, derived from post-consumer and post-industrial waste, is increasingly vital in sustainable manufacturing. Handling and processing RPE in industrial settings involves several best practices to ensure quality and efficiency while minimizing environmental impact. One of the primary considerations is the source and quality of the recycled material. Contaminants such as food residues or other non-plastic materials can significantly affect the properties of recycled polyethylene, making thorough sorting and cleaning essential. Advanced sorting technologies, including infrared and x-ray systems, can enhance the accuracy of contaminant removal, leading to higher-quality outputs.
In the processing phase, it’s crucial to manage the thermal conditions meticulously. Recycled polyethylene often has varying melting points and viscosities compared to virgin polyethylene, which can complicate the extrusion and molding processes. Implementing precise temperature controls and monitoring equipment helps maintain consistent material properties and avoids degradation that could weaken the final products. Additionally, blending RPE with virgin resin or other additives might be necessary to achieve the desired physical characteristics and performance standards.
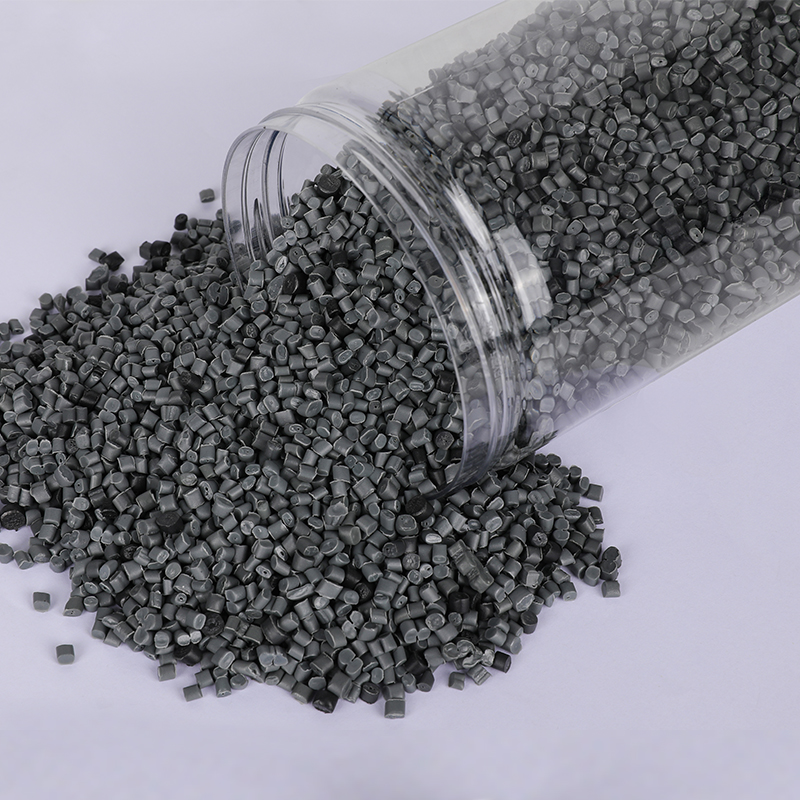

From a commercial perspective, the integration of recycled polyethylene into manufacturing processes can impact overall production costs. While RPE generally costs less than virgin polyethylene, the need for additional processing steps and potential quality control measures can offset these savings. Manufacturers must balance these factors by investing in efficient recycling technologies and exploring economies of scale to enhance the commercial value of RPE. This approach also contributes to a positive environmental footprint by conserving energy and reducing waste compared to the production of new plastics.
Historically, the development of RPE recycling practices has evolved significantly. Early recycling efforts focused on basic sorting and remelting, but advancements in technology and increased regulatory pressure have driven improvements in processing techniques. Government policies and public awareness campaigns have played crucial roles in shaping the industry, encouraging more widespread adoption of recycled materials and pushing for higher standards in recycling practices. As these practices continue to advance, they will play a pivotal role in the broader efforts to reduce plastic waste and promote sustainable manufacturing practices.
As China PCR Recycled Plastic Granules Factory, We always adhere to the experience and philosophy of "keeping up with the times, constantly innovating, developing efficiently, and cooperating for mutual benefit"

Address: No.11, Wangzhuang Section, Provincial Road 01, Daqiao New Area, Economic Development Zone, Haiyan County, Jiaxing City, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone: +86-18058285678
Fax: +86-0573-86868101
E-mail: [email protected]
SUNRISE GROUP(Overseas Exclusive Agent)
www.sunrisechemical.com
2024 ICIS Global Chemical Distributor Top 8
Export Sales Manager:Helen Zhang
Mob/Whatsapp: +86 19883063465
Email: [email protected]
Copyright © Jiaxing Anyiju Plastic Industry Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English