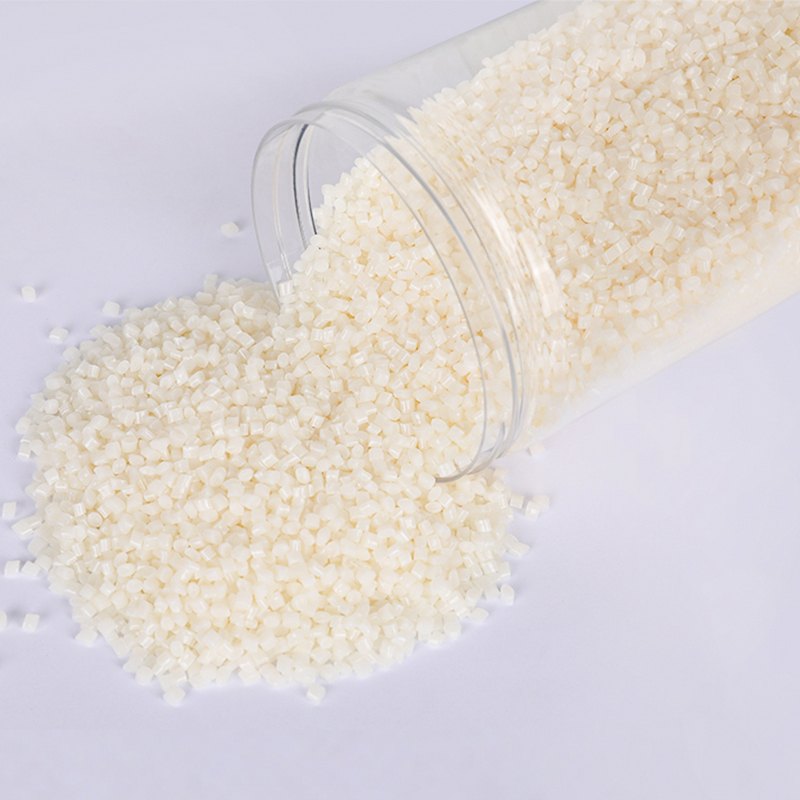
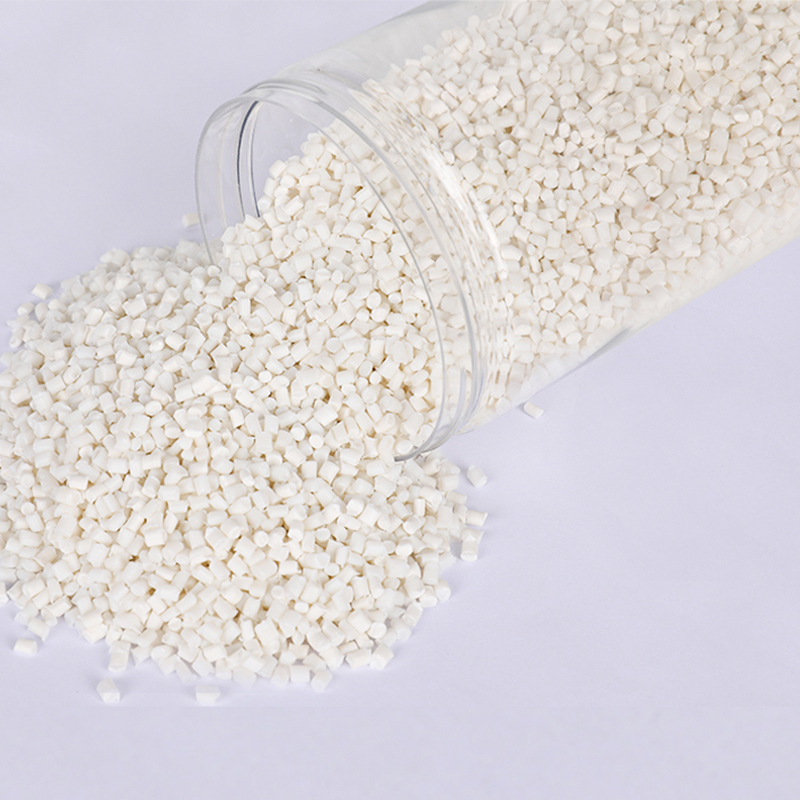
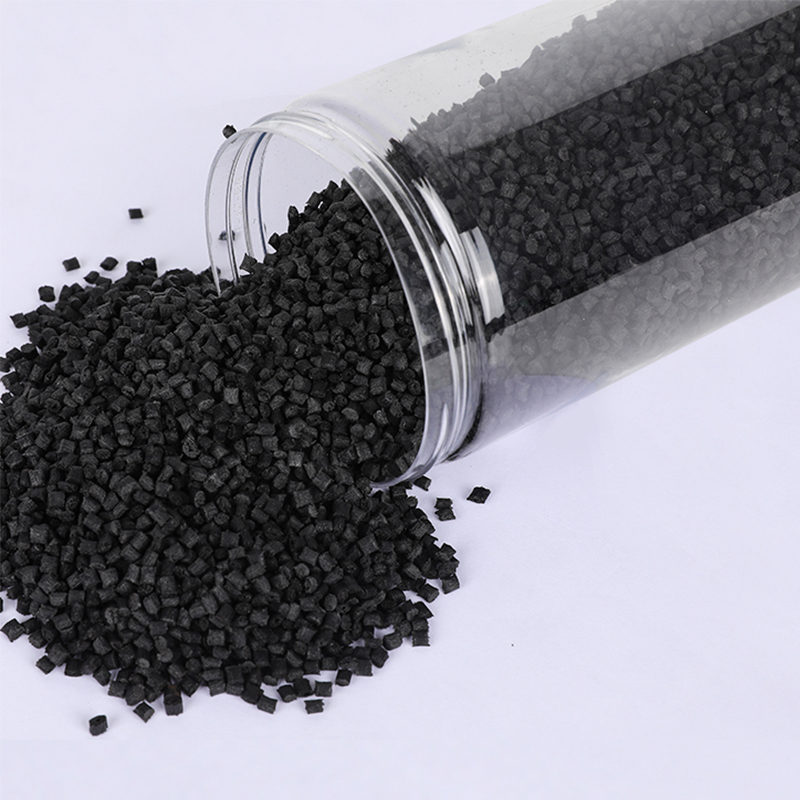
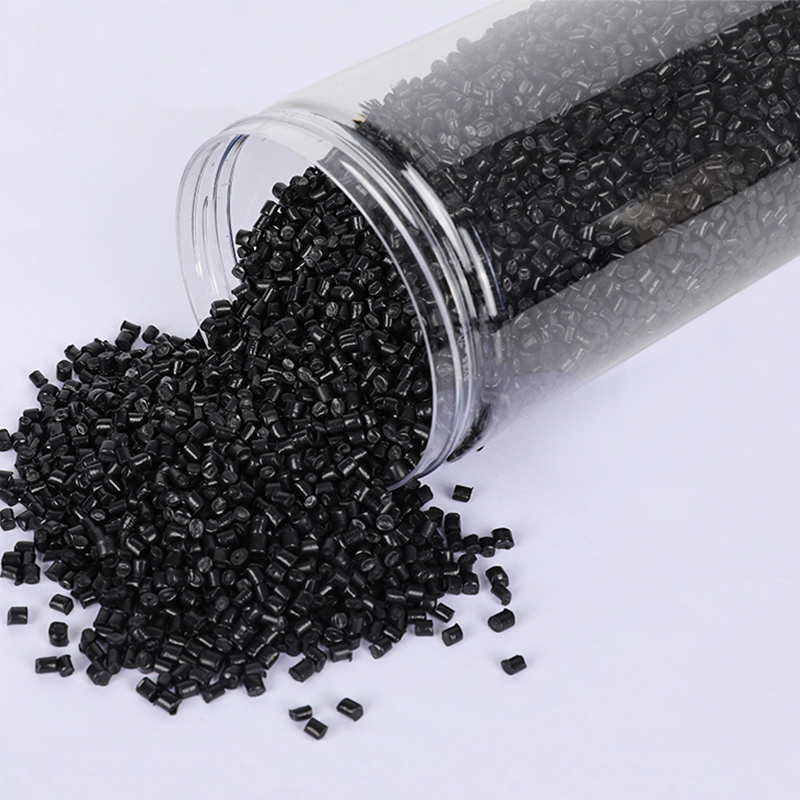
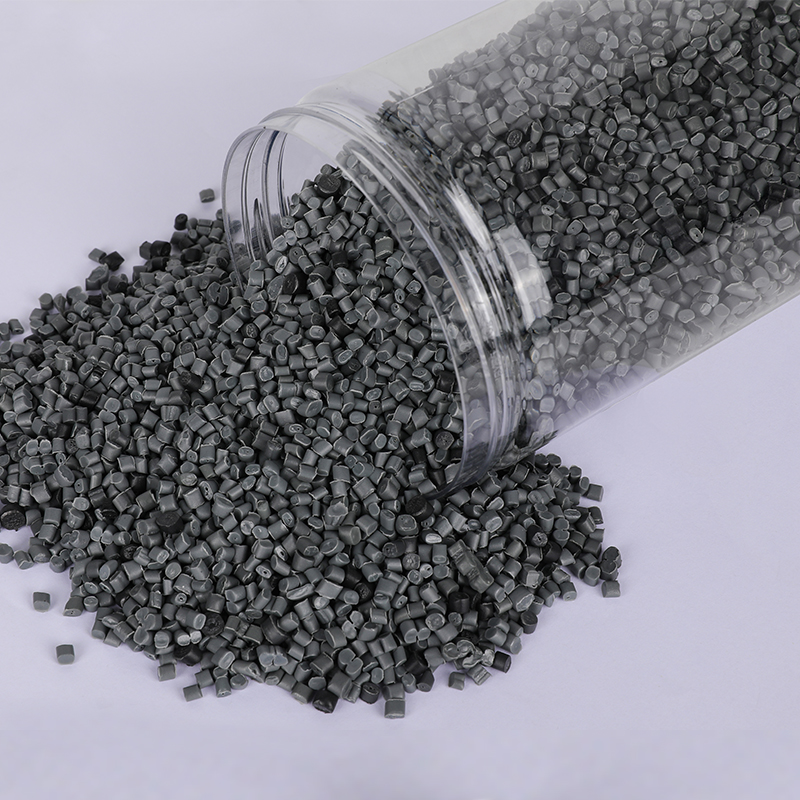
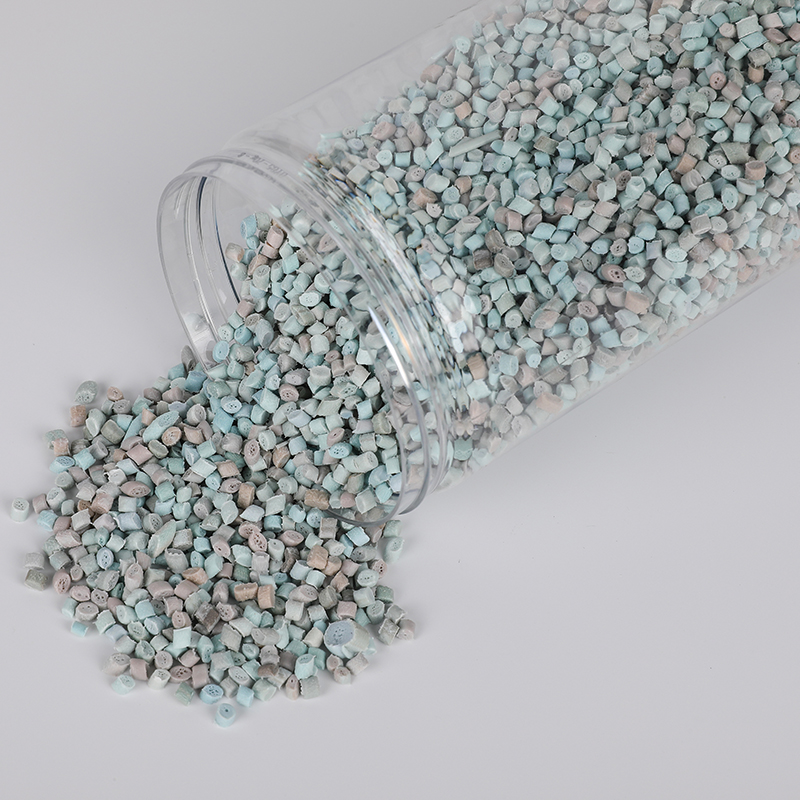
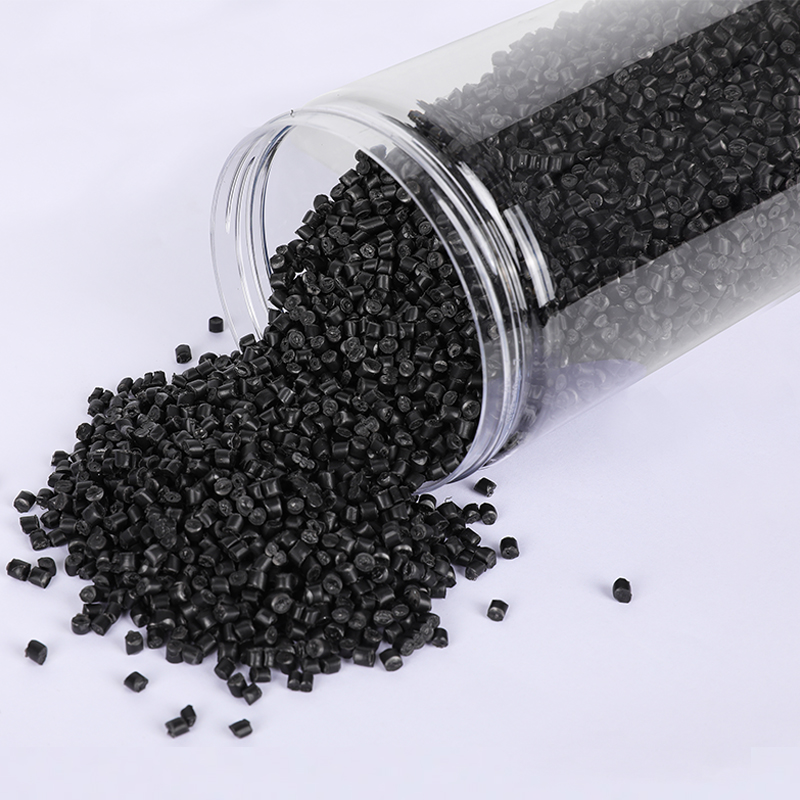
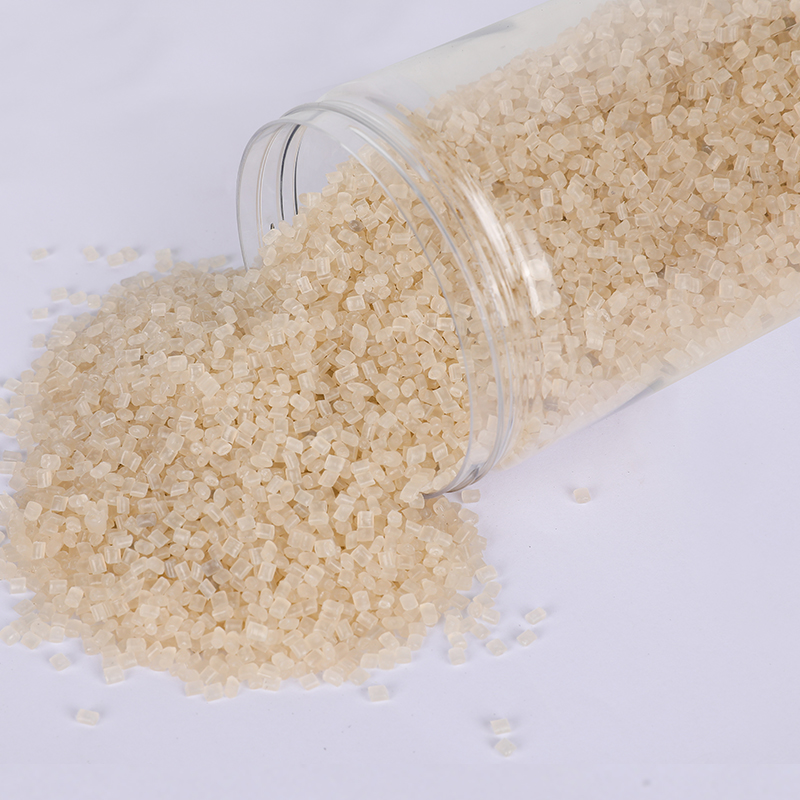
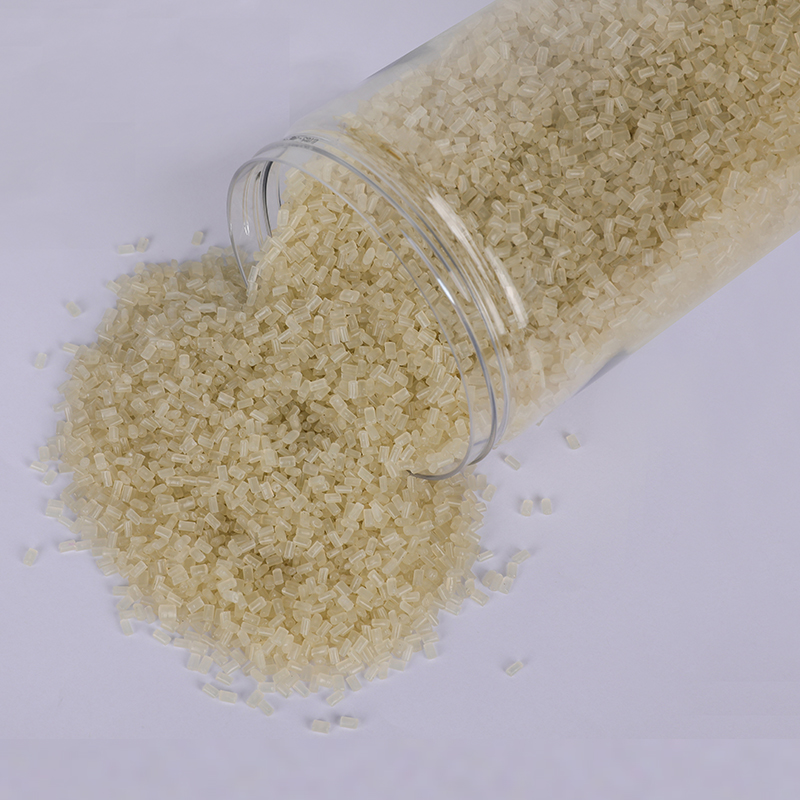
We have got a high reputation in both domestic and overseas markets.

Jiaxing Anyiju Plastic Industry Co Ltd
ANYIJU is a China PIR Plastics Polypropylene Resin Raw Material suppliers and PIR Plastics Polypropylene Resin Raw Material Factory with a strong technical team and several manufacturing lines that have been working in modified plastics for over 20 years. The products produced by ANYIJU can be used in a wide range of fields, including chemical, automotive, light industry, textile, machinery and household appliances. In addition, special modified materials based on customer requirements can also be designed, developed and produced by plants.
ANYIJU is also certified through the GRS Global Recycling Standard, Product Carbon Footprint Certification, ISO9001 Quality Systems Certification, 14001 Environmental Systems Certification, and other certifications. Adhering to the experience and philosophy of "keeping up with the times, constantly innovating, developing efficiently, and cooperating for mutual benefit" and relying on rich production experience and an excellent technical team, ANYIJU will definitely make us your partner of choice.
Sincerely welcome you to visit, inspect, and cooperate with our company.
WHY WE ARE SO TRUSTED
News
Product Related Knowledge Expansion
The source of post-industrial recycled polypropylene (PIR PP) resin is industrial waste generated during the manufacturing process. Post-industrial recycling specifically refers to the recycling of waste materials that are generated within the manufacturing or industrial processes, as opposed to post-consumer recycling, which involves recycling materials that have been used by consumers.
The industrial waste that contributes to post-industrial recycled polypropylene resin can originate from various manufacturing sectors and processes. Some common sources include:
Manufacturing Scrap:
During the manufacturing of polypropylene-based products, there may be leftover or excess materials, such as trimmings, rejected parts, or off-spec products. These materials can be collected and recycled to produce PIR PP resin.
Production Offcuts:
Offcuts or excess materials generated during the fabrication of polypropylene components or products contribute to post-industrial waste. These materials can be recycled to reclaim the polypropylene for reuse.
Injection Molding Waste:
Injection molding, a common manufacturing process for plastic products, can generate waste in the form of sprues, runners, and defective parts. The polypropylene waste from injection molding processes can be collected for recycling.
Film and Sheet Production Waste:
Industries involved in the production of polypropylene films and sheets may generate waste during the manufacturing process. This waste can include trimmings and rejected materials that can be recycled.
Extrusion Waste:
Extrusion processes, such as profile extrusion or sheet extrusion, may produce waste materials that can be recycled. This can include offcuts, rejects, or materials that do not meet quality standards.
Thermoforming Scrap:
Thermoforming processes, used to create products from plastic sheets, can generate scrap materials. The waste generated during thermoforming can be collected and recycled.
Fiber and Textile Production Waste:
In industries involved in the production of polypropylene fibers and textiles, waste materials generated during the manufacturing process can be recycled.
The specific sources of post-industrial recycled polypropylene can vary depending on the type of manufacturing involved and the products being produced. Recycling these industrial waste materials helps to reduce the environmental impact associated with manufacturing processes, conserves resources, and promotes a more sustainable approach to plastics production.
Post-industrial recycled polypropylene (PIR PP) resin is sourced from various industries and manufacturing processes that generate waste during their production activities. Some of the types of industries and processes that commonly contribute to post-industrial waste suitable for PIR PP recycling include:
Injection Molding:
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process for producing plastic parts. Industries involved in injection molding may generate waste in the form of sprues, runners, and rejected or excess parts.
Extrusion:
Extrusion processes, such as profile extrusion, film extrusion, and sheet extrusion, produce plastic products by melting and forming plastic material. Trimmings, offcuts, and rejected products from extrusion processes contribute to post-industrial waste.
Blow Molding:
Blow molding is commonly used to manufacture plastic bottles, containers, and other hollow products. Waste generated during the blow molding process, such as excess material or rejected products, can be recycled.
Thermoforming:
Thermoforming involves heating plastic sheets to a pliable temperature and then forming them into specific shapes. Scrap material and rejected parts generated during thermoforming contribute to post-industrial waste.
Fiber and Textile Production:
Industries involved in producing polypropylene fibers and textiles may generate waste during spinning, weaving, or other manufacturing processes. This waste can be recycled to produce PIR PP resin.
Automotive Manufacturing:
The automotive industry uses polypropylene in various components such as interior parts, bumpers, and panels. Manufacturing processes in the automotive industry can generate polypropylene waste suitable for recycling.
Packaging Manufacturing:
Companies producing polypropylene-based packaging materials, such as films, sheets, and containers, generate waste during the manufacturing process. This waste is a potential source for post-industrial recycling.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English